Telemetry Radio
The standard aircraft configuration utilizes an ISM serial radio for control, telemetry, and PPM passthrough from the hand controller. The radio range is variable based on a number of environmental and operational factors and equipment selection. The aircraft uses omnidirectional dipole antennas. Secondary radios can be installed in dedicated drop-in module compatible mounts under the wings.
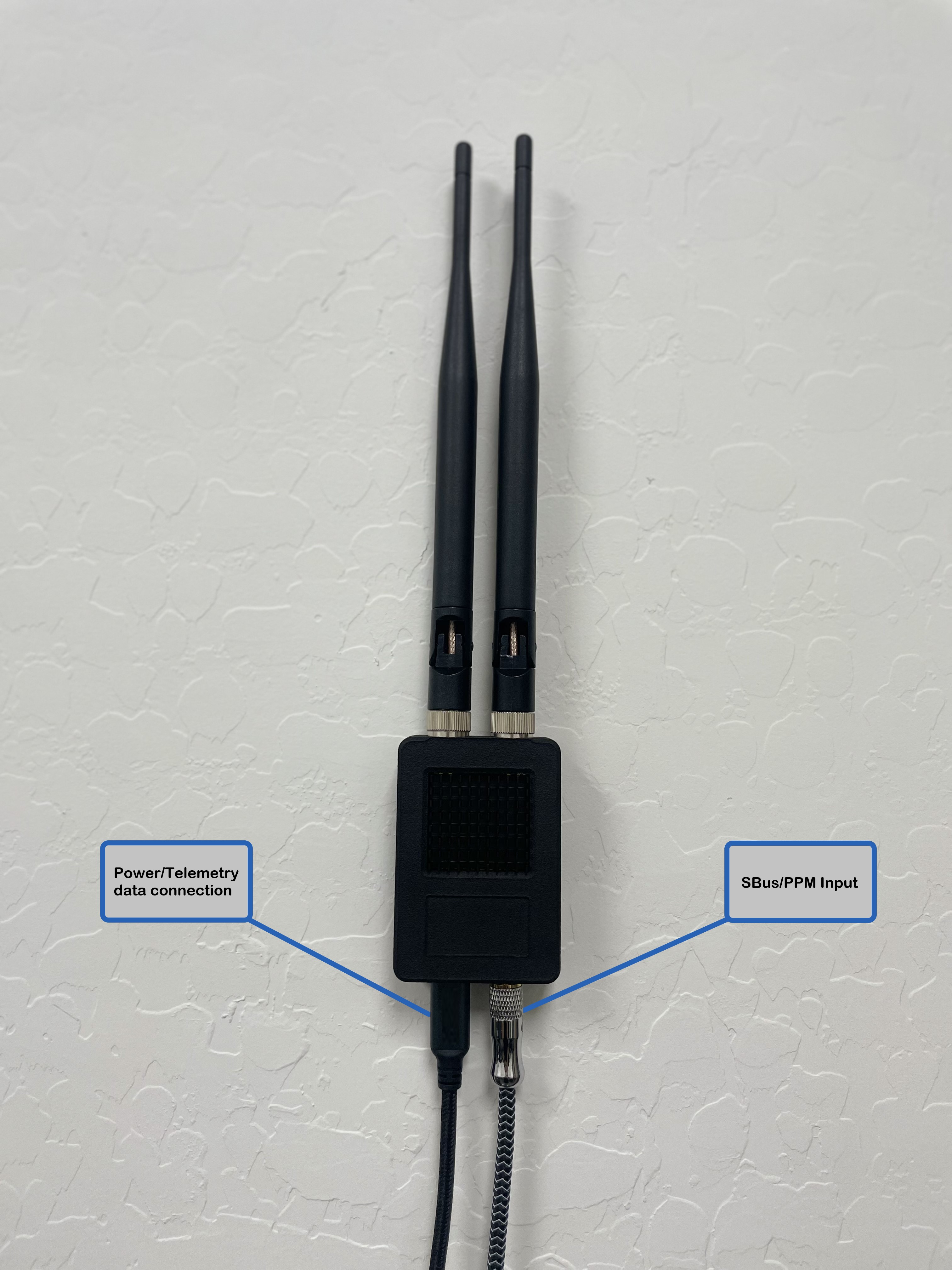
Radop Specs
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Ground Radio | RFD 900 |
| Encryption | AES Hardware Encryption |
| Data Rate | 250 kbit/sec |
| Power | 1W (configurable) |
| Latency | ~7ms |
| Frequency | 900-928 mhz |
| Antenna Options | Omni, Directional |
Hand Controller
The safety pilot can optionally fly the aircraft, manually or assisted, and change modes independent of the operator using the handheld controller. Most commands from the controller are sent through the telemetry radio instead of using the internal RF module located in the transmitter itself.
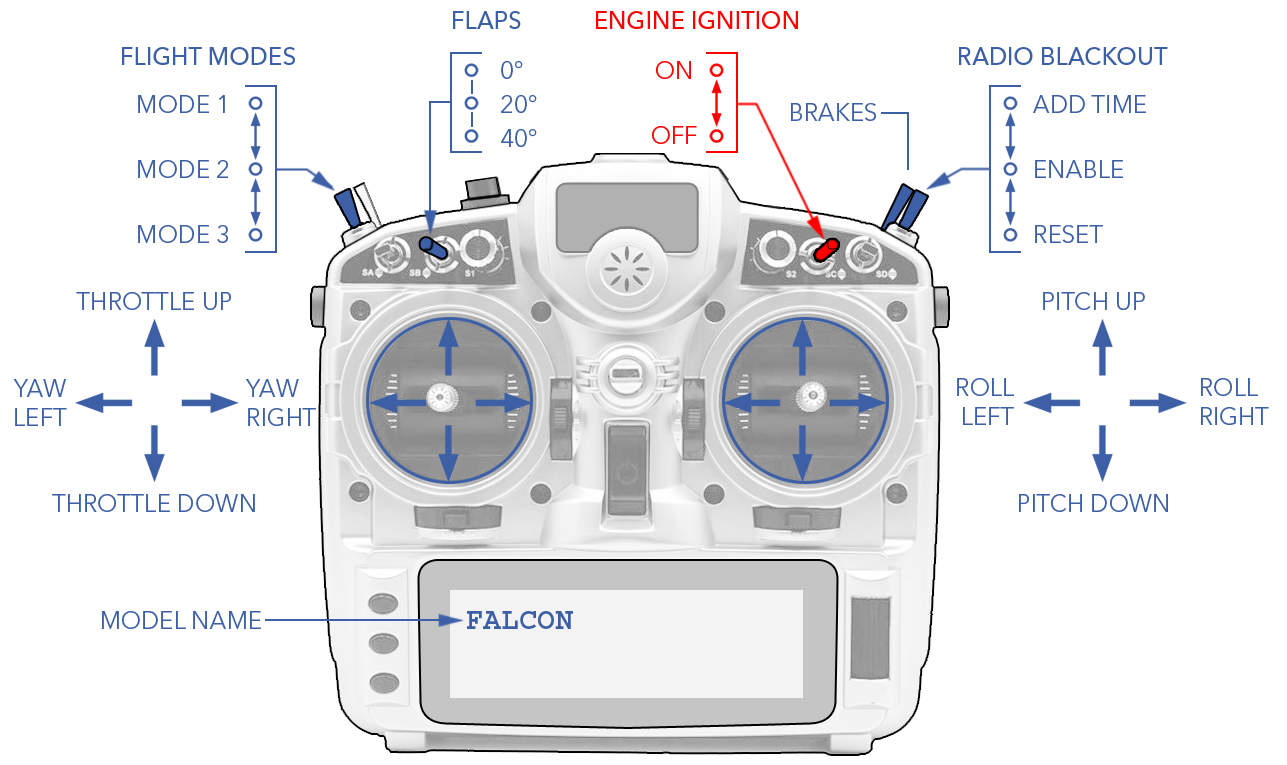
Flying with the hand controller can be useful for in-flight interventions or when the launch and recovery situation is challenging, but using the controller should strictly be reserved for experienced safety pilots.
Hand Controller Specs
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Controller | FrSky Taranis X9D |
| Firmware | OpenTX |
| Channels | 24 |
| Protocol | PPM Passthrough |
| Internal RF | 2.4Ghz |
| Receiver Compatibility | ACCST D16, ACCESS |